Many of us have heard the term CBDC, means Central Bank Digital Currency. Recently in India, RBI (Central Bank of India) have launched (1st Dec, 2022) the pilot version. This makes me the curiosity to get to know more on CBDC what it is, why it is, how it work.
What CBDC
Basically CBDC is the general term like currency, as every country have their own currency like India has Rupee, USA has dollar, so this as collectively called as currency. Same like each country planning to release their own digital currency and that will be released by their respective country’s central bank, as collectively these digital currencies are called as CBDC.
Mostly the value of the digital currency will be equal to their fiat value. Since each country’s central bank releasing the coins, these are legal and regulated.
Why CBDC
In evolution of money, it started from barter concept to gold, later it evolved to metal coins and now its cash. As a next move, it will be the virtual coins.

In current situation, crypto currencies and stable coins are more popular which may diminish country’s monetary. In this situation each countries are in the position to release their own digital coins.
Apart from this, as experience of using cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, many people felt the ease use, secure, and quick transaction which reduce the time consumption, same features apllicable for CBDCs.
By making the physical currency note into digital currency, it may lead to operational cost reduction.
Since this CBDC is another form of payment, obviously it will increase the financial inclusion.
This digital way will add efficiency to settlement system and also make cross border payment easy.
Also few countries like India, are planning to release the offline feature through which we can make payment even the internet is not available like rural areas or hill stations. As a hint, this may be achievable by keeping some limitations of each user’s account, and up to that they can make offline payment. Once they connected back to internet this will get synced with the central database.
Above are the key motivations of CBDC, further will see the CBDC value by comparing with India’s CBDC (Digital Rupee).
CBDC Value
Will consider India’s CBDC – Digital Rupee for this.
Instead of printing money, the central bank issues electronic coins backed by the full faith and credit of the government.
It has equivalent value as physical Rupee and this CBDC is another form of currency, not an replacement of the note.
If you have 1 Digital Rupee in your e-wallet, that is equivalent to 1 Rupee physical coin in your hand, so its 1:1.
Types of CBDC
Basically two types are available :
Wholesale CBDC (CBDC-W) :
- This coin can be used only by financial companies like bank with restricted usage.
- Main intent is for inter-bank settlement transfers.
Retail CBDC (CBDC-R) :
- This coin can be used by general people, business people like P2P or P2M and non-financial companies.
- It’s like normal money transfer as we do via UPI.
As of India, RBI is planning to introduce both types of CBDC.
Models for Issuance and Management of CBDC
Direct Model :
- •In this model, RBI has responsibility to issuance of the coins to public, account-keeping, transaction validations.
- This may lead to over burden to central bank.
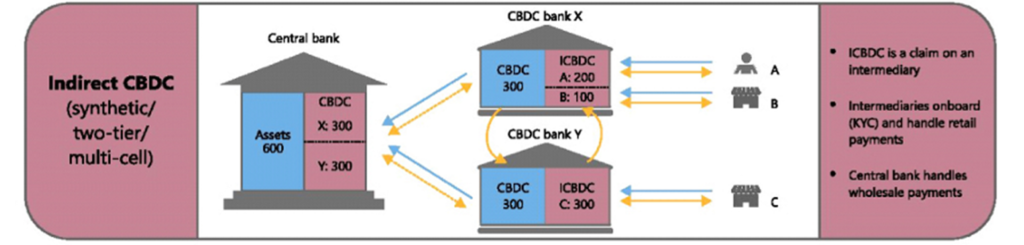
Indirect Model :
- In this model, banks will act as intermediates where RBI will issue CBDC indirectly to public via bank.
- Account keeping, validations, disputes everything will take care by bank.
- Here the wholesale transactions alone will happen between RBI and the intermediates.
- Currently, physical Rupee following the Indirect model, same like RBI planned to follow the same for Digital Rupee.
Technology choice
Couple of choices available :
- Centrally Controlled Technology : Meaning in short, full power will be in one’s hand. If needed they can manipulate the data.
- Distributed Ledger Technology : Meaning in short, there is no one hand power, and can’t able to manipulate data easily.
More than 88% of CBDC projects, at pilot or production phase, use blockchain as the underlying technology.
Blockchain technology brings several benefits to CBDC developments like, transfer ownership in a secure way, utilizing smart contracts and more.
However so far, RBI planned to follow Centrally controlled technology majorly. Still RBI looking for the use case where Distributed technology can be utilized.
Digital Rupee will be maintained/handled via an app, provided by respective bank which will be act as a wallet. Here wallet will be linked with our mobile number.
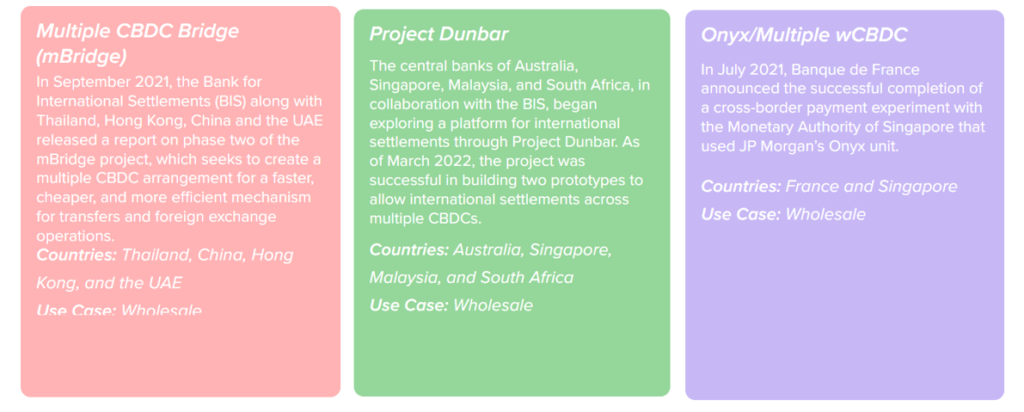
Cross Border Projects
Many countries are exploring the CBDC. Financial sanctions on Russia makes many countries to explore alternate international payment systems.
BIS institution were collaborating with many countries for cross border projects.
As per the World Bank, India is the world’s largest recipient of remittances as it received $87 billion in 2021 with the United States being the biggest source. However, as of now, RBI yet to reach this level.
Around 10 cross border projects are currently there, few are below :
Crypto VS CBDC
Crypto is volatile where CBDC is less and has government backup.
The proliferation of crypto assets can pose significant risks related to Financing of Terrorism.
Crypto is legal in India, where Digital Rupee is also legal.
Most of the cryptocurrencies utilize public Blockchain (DLT), For CBDC, most of them follow private blockchain or centrally maintained.
UPI VS CBDC
UPI transactions involves banks as intermediators where as in CBDC there is no intermediation of banks.
UPI : If A send money to B, here, money flow will happen between A’s bank (HDFC) to B’s bank (ICICI) and then B will get notified.
CBDC : If A send money to B, here, money flow will happen between A’s wallet to B’s wallet and there wont be any intermediate banks involvement.
RBI claiming that the Digital Rupee assures the anonymity, also it can be used Offline.
CBDC Status – worldwide
So far, 119 counties are working for their CBDC. Among that, The Bahamas, Jamaica, Nigeria, and 8 Caribbean countries launched their CBDCs.
The Digital Yuan project in Mainland China has already reached an advanced level of trialing, with more than 2 billion yuan (~$300m) in transactions.
We an check the status of each CBDC from Atlantic Council website.
Digital Rupee – Pilot Release
1st Nov, 2022, RBI released the pilot version of CBDC-W and on 1st Dec, 2022 released the pilot version of CBDC-R.
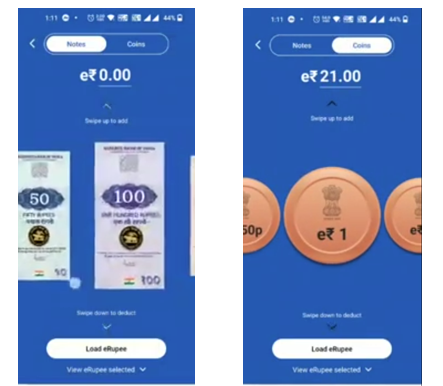
For CBDC-R, an app needs to be installed which will get linked with our mobile number will act as a wallet.
Digital Rupee are available in same denominations as like physical notes and coins like 10s, 50s, 100s, 500s … in notes and 1s, 2s … as coins.
Following activities can be done by using this app : Load, Redeem, Send, Receive.
Load : Conversion of Rupee into Digital Rupee, via from our bank account to e-wallet.
Redeem : Moving from e-wallet to bank account.
Send : We can send money to any person or we can buy any products by scanning the QR code.
Receive : Same like, we can receive Digital Rupee from anybody.
Each digital note/coin will have serial number.
Above article have explained as of (Dec, 2022) the information available. During each CBDC development, progress may get changed. Still many internal working technique are need more clarity, this may clarified once the CBDCs are fully rolled out.
As for India’s RBI, as of now they started the pilot testing, still need to gather more experience which helps in smooth rollout.